In this tutorial, we will discuss all the steps required to install Android Platform Tools and SDK Manager on Windows 10. This tutorial provides the steps for Windows 10, though the steps should be the same on other versions of Windows.
This post is useful for the developers using Android Platform Tools and SDK manager without installing Android Studio for the use cases including hybrid app development using Ionic. It also assumes that a valid JAVA_HOME environment variable exists pointing to the installation directory of Java.
You can follow How To Install Java 8 On Windows 10, How To Install Java 11 On Windows, How To Install Java 15 On Windows, or How To Install OpenJDK 15 On Windows to install Java on Windows. In case you are interested in developing Android applications using Android Studio, you can also follow How To Install Android Studio On Windows.
Step 1: Download SDK Tools
Open the download tab of Android Studio and scroll down to the Command line tools only section. This section shows various options for downloading the SDK tools, as shown in Figure 1.

Fig 1
Click the first link with the download option for Windows, as highlighted in Figure 1. It will ask you to accept the terms and conditions, as shown in Figure 2.

Fig 2
Go through the details, agree on the terms and conditions and click the Download Button to start the download.
Step 2: Install Command Line Tools
In this step, we will install the Android Command Line Tools on Windows 10. Create the directory android-sdk at your preferred location and extract the content of the downloaded SDK Tools zip to this directory. Make sure that the extracted content is available within the android-sdk directory created by us as shown in Fig 3.

Fig 3
Step 3: Install Platform Tools
In this step, we will install the Android Platform Tools on Windows 10. To do so, follow the same steps as for Android SDK Tools, using the download link shown in Figures 4, 5, and 6.

Fig 4
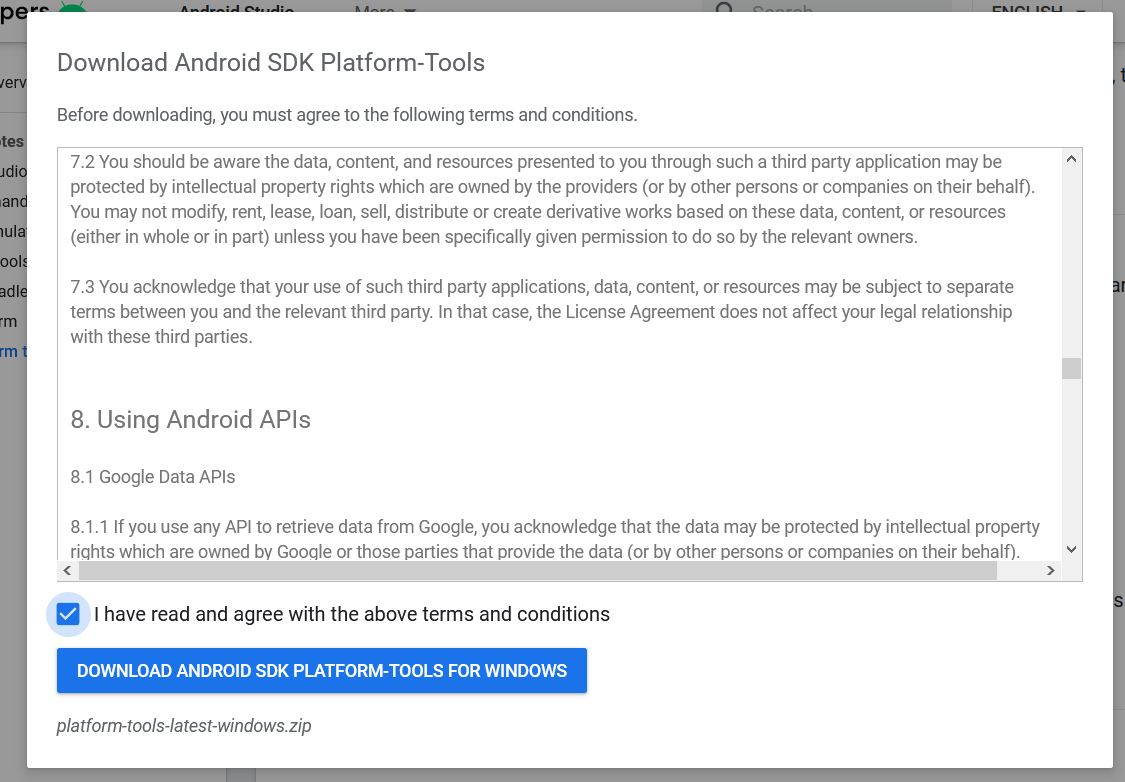
Fig 5

Fig 6
Step 4: Configure Environment Variable
Right-click the My Computer or This PC on the desktop and click the Properties Option. Now click the Advanced system settings. It will show the System Properties dialog having Advanced Tab options as shown in Fig 7.

Fig 7
Click the Environment Variables Button and click the New Button in the first section. Set the Variable Name field to ANDROID_HOME and Variable Value to the android-sdk directory created by us in the previous step.
Similarly, also configure the environment variable ANDROID_SDK_ROOT to the android-sdk directory.
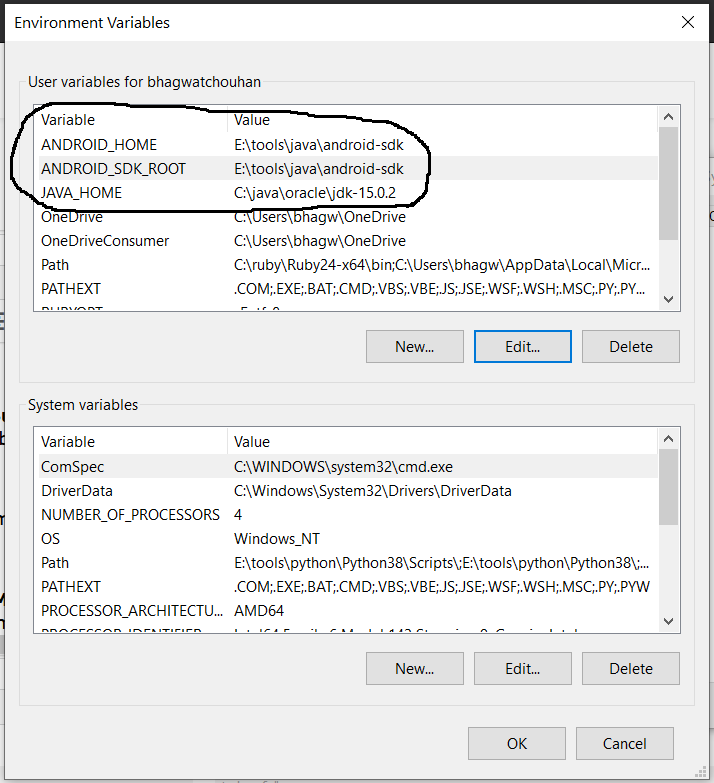
Fig 8
Step 5: Configure Commands
In previous steps, we have downloaded and extracted the Command Line Tools and Platform Tools to the android-sdk directory. Both the tools provide several command-line utilities which we need to run by going to the appropriate directory having the executable files.
We can make these commands available at the system level without going to these directories by adding the path to tools, tools\bin, and platform-tools to the system path as shown in Fig 9. Make sure that these executables do not break other commands having the same name before adding these paths to the PATH environment variable.

Fig 9
Now open the Command Prompt and check the ADB and SDK Manager versions as shown in Fig 10. You might be required to restart the system to apply the environment variables set by us.
# Check adb version adb --version
# It must show the installed adb version Android Debug Bridge version 1.0.41 Version 31.0.0-7110759 Installed as E:\tools\java\android-sdk\platform-tools\adb.exe
# Check sdkmanager version sdkmanager --version
# It will show the error as shown below Error: Could not determine SDK root. Error: Either specify it explicitly with --sdk_root= or move this package into its expected location: <sdk>\cmdline-tools\latest\
We can see that the ADB command works well and shows the version details, but the sdkmanager shows an error - "error: could not determine sdk root. error: either specify it explicitly with --sdk_root= or move this package into its expected location: <sdk>\cmdline-tools\latest\" since it expects the Command Line Tools in a version-specific directory. Now open the source.properties file from the cmdline-tools directory to check the version. It will show the version details as shown below.
Pkg.Revision=3.0 Pkg.Path=cmdline-tools;3.0 Pkg.Desc=Android SDK Command-line Tools
Now move all the files to the directory cmdline-tools/3.0 as shown in Fig 10.

Fig 10
Also, update the system path as shown in Fig 11.

Fig 11
Now close and open the Command Prompt. Also, check the ADB and SDK Manager versions as shown in Fig 12.

Fig 12
Step 6: Using the SDK Manager
List - We can list the installed and available packages and images using the list command as shown below.
// List all the installed and available platforms, system images and other resources sdkmanager --list
// Output should look like Installed packages:=====================] 100% Computing updates...
Path | Version | Description | Location
------- | ------- | ------- | -------
platform-tools | 31.0.0 | Android SDK Platform-Tools 31 | platform-tools\
Available Packages:
Path | Version | Description
------- | ------- | -------
add-ons;addon-google_apis-google-15 | 3 | Google APIs
...
...
// We can see that it shows the tools and platform-tools installed by us
Install Platform - Use the below-mentioned command to install the Android 10 (API level 30) using the SDK manager.
# Go to the SDK Tools bin directory to access sdkmanager # Start download the most recent package sdkmanager "platforms;android-30"
It will ask to accept the terms and conditions as shown in Fig 13. Enter y and hit Enter Key to accept the terms and conditions. This command creates the directory platforms within android-sdk and installs the package android-30 having all the required files to run the emulator for Android 10.
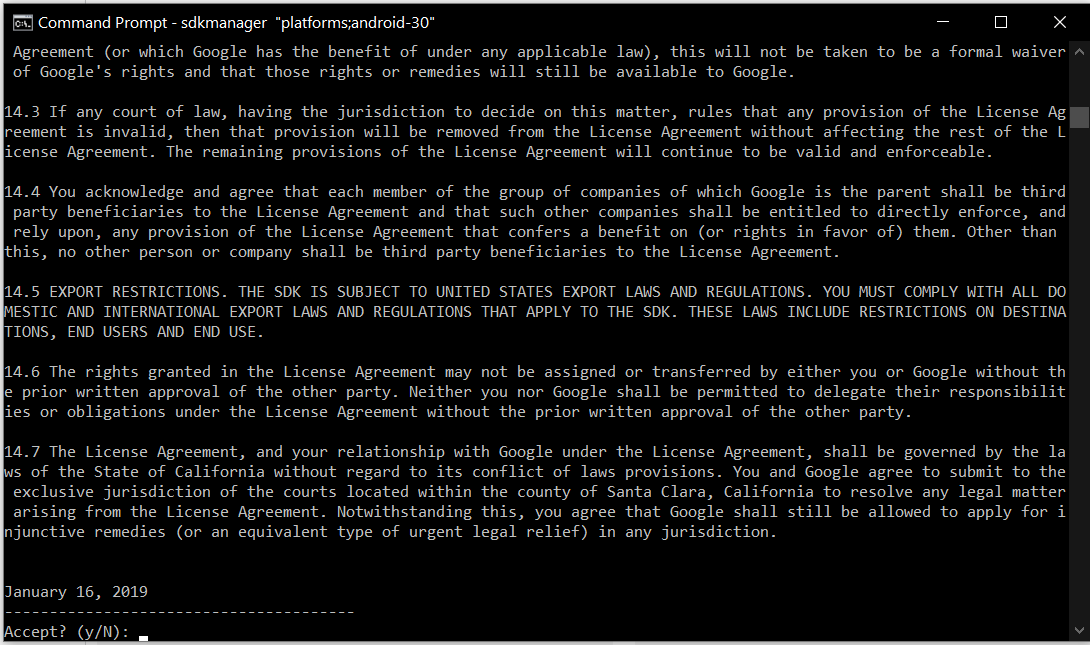
Fig 13
If we again check the installed packages, the list command shows the installed options as shown below.
sdkmanager --list
Installed packages:=====================] 100% Computing updates...
Path | Version | Description | Location
------- | ------- | ------- | -------
platform-tools | 31.0.0 | Android SDK Platform-Tools 31 | platform-tools\
platforms;android-30 | 3 | Android SDK Platform 30 | platforms\android-30\
Available Packages:
Path | Version | Description
------- | ------- | -------
add-ons;addon-google_apis-google-15 | 3 | Google APIs
add-ons;addon-google_apis-google-16 | 4 | Google APIs
...
...
Update SDK Manager - Update the SDK manager using the below-mentioned command.
sdkmanager --updateAdd System Image - We can add system images from available images shown by the list command using the SDK manager as shown below. We are adding the most recent default 64-bit system image.
// Install default system image for platform android-30 sdkmanager "system-images;android-30;google_apis;x86_64"
Accept the License Agreement to complete the download.
Several projects need Google Play Services. We need system images specific to Google Play Services, as shown below.
// Install Google Play Services system image sdkmanager "system-images;android-30;google_apis_playstore;x86_64"
Accept the License Agreement to complete the download.
Install Emulator - We need to install the emulator before creating the AVD using SDK Manager.
// Install Emulator sdkmanager --channel=3 emulator
Accept the License Agreement to complete the download.
Install Build Tools - Install the most recent build tool listed by
// Install Build Tools sdkmanager "<build tools version>"
// Example sdkmanager "build-tools;30.0.3"
Step 7: Using the Emulator and AVD Manager
Create Android Emulator - Create the emulator using the system image downloaded in the previous step as shown below. Replace <emulator name> with the actual name preferred by you.
// Create the emulator using default system image avdmanager create avd -n <emulator name> -k "system-images;android-30;google_apis;x86_64" -g "google_apis"
// Example: avdmanager create avd -n emulator30 -k "system-images;android-30;google_apis;x86_64" -g "google_apis"
// Create emulator using Google Play Services system image avdmanager create avd -n <emulator name> -k "system-images;android-30;google_apis_playstore;x86_64"
// Example: avdmanager create avd -n emulator30ps -k "system-images;android-30;google_apis_playstore;x86_64"
The above commands ask a bunch of questions to configure the AVD if we choose the custom hardware profile option. We have excluded the details of these options from this tutorial since these configuration details depend on the actual needs. After completing all the configurations, it creates the AVD using the name provided by us while configuring it.
Similarly, we can also install the AVD of older versions as shown below.
// Create the emulator using default system image avdmanager create avd -n <emulator name> -k "system-images;android-29;default;x86_64" -g "default"
// Example: avdmanager create avd -n emulator29 -k "system-images;android-29;default;x86_64" -g "default"
// Create emulator using Google Play Services system image avdmanager create avd -n <emulator name> -k "system-images;android-29;google_apis_playstore;x86_64"
// Example: avdmanager create avd -n emulator29ps -k "system-images;android-29;google_apis_playstore;x86_64"
List Android Emulators - Now go to the tools directory on the command line and check the installed platform as shown below.
Notes: Add Emulator to the system path as shown in Fig 14.

Fig 14
Close and re-open the Command Prompt to check the AVDs created by us in the previous steps.
// List the available emulators emulator -list-avds
// Output default28 emulator30 emulator30ps
It will list all the AVDs installed by us.
Run Emulator - We can run the emulator created by us as shown below.
// Run Emulator emulator -avd <emulator name>
// Example emulator -avd emulator30
The emulator will take some time to completely launch the AVD. The final results should look similar to Fig 15.
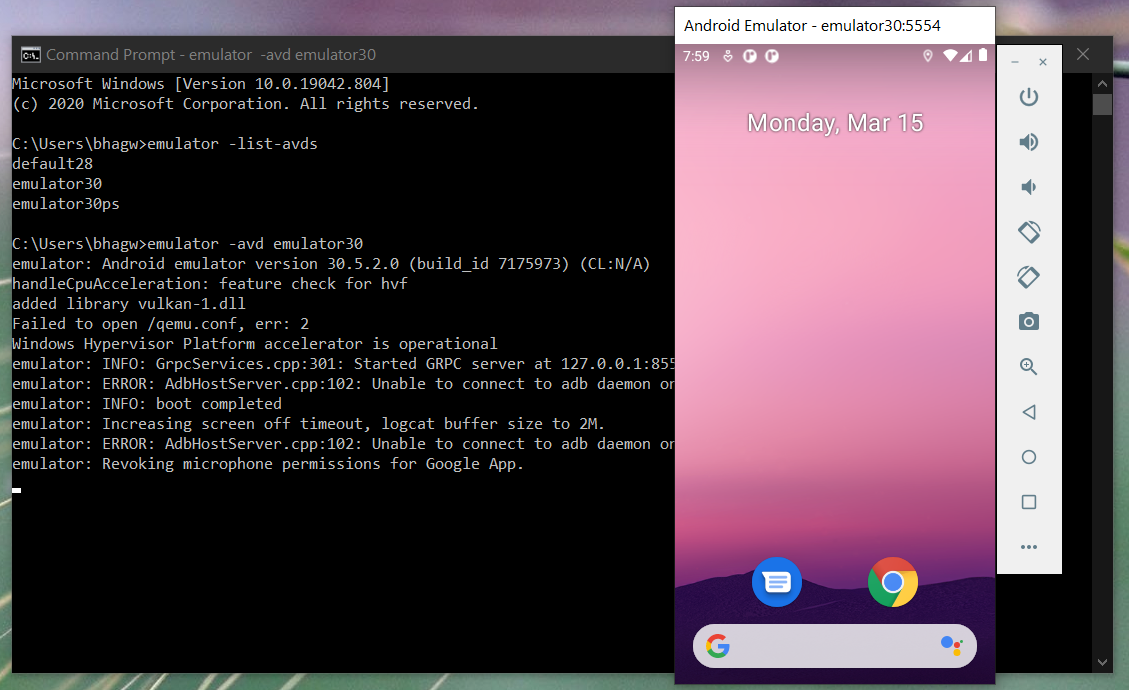
Fig 15
Delete Emulator - We can also delete an existing emulator as shown below.
// Delete Emulator avdmanager delete avd -n <emulator name>
Summary
This tutorial provided all the steps required to install Android Platform Tools and Android SDK Manager on Windows 10. It also provided the steps required to create and launch the AVDs using the Emulator.

