This tutorial provides complete steps to design a database schema of online shops and shopping carts to manage the users, products, reviews, carts, orders, and payments. It can be further used to develop an online shop and shopping cart based websites or applications.
The Entity Relationship Diagram or visual database design is shown below.
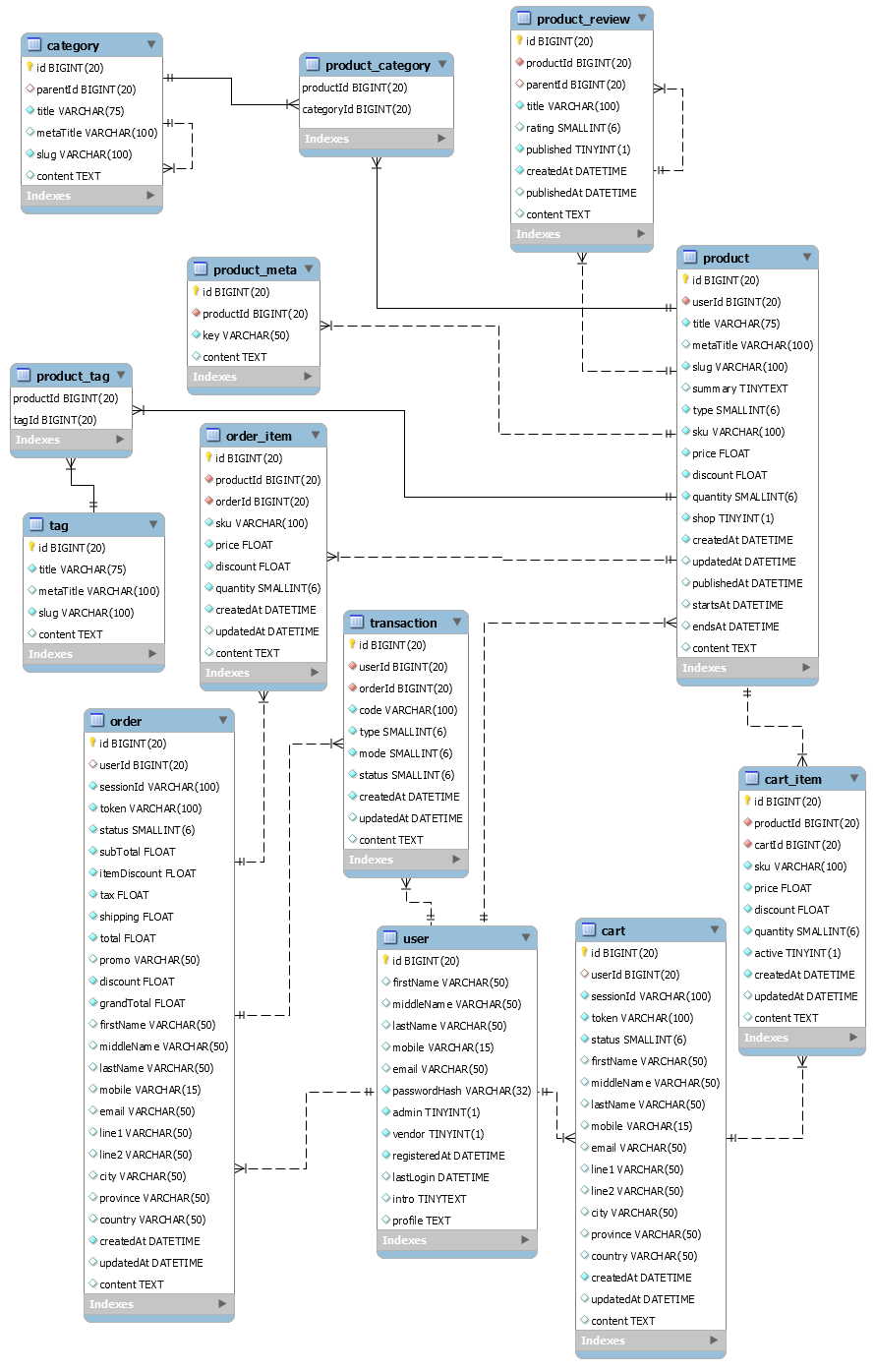
Online Shopping Cart
Notes: It allows guest orders to place the order without logging in. The security can be handled by following RBAC Database in MySql.
You can also visit the popular tutorials including How To Install MySQL 8 on Ubuntu, How To Install MySQL 8 on Windows, How To Install MySQL 8 With Workbench On Windows 10, RBAC Database in MySql, Blog Database in MySql, Quiz Database In MySQL, Poll & Survey Database On MySQL, and Learn Basic SQL Queries In MySQL.
Shop Database
The very first step is to create the Shop Database. It can be created using the query as shown below.
CREATE SCHEMA `shop` DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
I have used the character set utf8mb4 to support a wide range of characters.
User Table
In this section, we will design the User Table to store user information. The same table can be used to manage different types of users including admins and customers. It can also be used to relate the product creators(from the admin panel) and customer orders placed on the website. Users can track their own orders and track the status. Below mentioned is the description of all the columns of the User Table.
| Id | The unique id to identify the user. |
| First Name | The first name of the user. |
| Middle Name | The middle name of the user. |
| Last Name | The last name of the user. |
| Mobile | The mobile number of the user. It can be used for login and registration purposes. |
| The email of the user. It can be used for login and registration purposes. | |
| Password Hash | The password hash generated by the appropriate algorithm. We must avoid storing plain or encrypted passwords. |
| Admin | The flag to identify whether the user is an administrator. It's not required if RBAC tables are created by following the RBAC database design. |
| Vendor | The flag to identify whether the user can host a product in the shop. It's not required if RBAC tables are created by following the RBAC database design. |
| Registered At | This column can be used to calculate the life of the user with the application. |
| Last Login | It can be used to identify the last login of the user. |
| Intro | The brief introduction of the Vendor User to be displayed on the Product Page. |
| Profile | The vendor details to be displayed on the Product Page. |
The User Table with the appropriate constraints is as shown below.
CREATE TABLE `shop`.`user` ( `id` BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `firstName` VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL, `middleName` VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL, `lastName` VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL, `mobile` VARCHAR(15) NULL, `email` VARCHAR(50) NULL, `passwordHash` VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL, `admin` TINYINT(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0, `vendor` TINYINT(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0, `registeredAt` DATETIME NOT NULL, `lastLogin` DATETIME NULL DEFAULT NULL, `intro` TINYTEXT NULL DEFAULT NULL, `profile` TEXT NULL DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`), UNIQUE INDEX `uq_mobile` (`mobile` ASC), UNIQUE INDEX `uq_email` (`email` ASC) );
Product Table
In this section, we will design the Product Table to store the product data. Below mentioned is the description of all the columns of the Product Table.
| Id | The unique id to identify the product. |
| User Id | The user id to identify the admin or vendor. |
| Title | The product title to be displayed on the Shop Page and Product Page. |
| Meta Title | The meta title to be used for browser title and SEO. |
| Slug | The slug to form the URL. |
| Summary | The summary to mention the key highlights. |
| Type | The type to distinguish between the different product types. |
| SKU | The Stock Keeping Unit to track the product inventory. |
| Price | The price of the product. |
| Discount | The discount on the product. |
| Quantity | The available quantity of the product. |
| Shop | It can be used to identify whether the product is publicly available for shopping. |
| Created At | It stores the date and time at which the product is created. |
| Updated At | It stores the date and time at which the product is updated. |
| Published At | It stores the date and time at which the product is published on the Shop. |
| Starts At | It stores the date and time at which the product sale starts. |
| Ends At | It stores the date and time at which the product sale ends. |
| Content | The column used to store the additional details of the product. |
It uses the column quantity to track the stock available in the product inventory to keep the design simple. It might be required to specify the quantity by several columns to cover a wide range of products. The possible columns could be sellQuantity, sellUnit, stockQuantity, and stockUnit where the sellQuantity and sellUnit can be used to be displayed on the Shop for the buyers and the stockQuantity and stockUnit can be used to track the inventory. It might also be required to convert the sellUnit to stockUnit while updating the inventory on placing the order. The Product Table with the appropriate constraints is as shown below.
CREATE TABLE `shop`.`product` (
`id` BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`userId` BIGINT NOT NULL,
`title` VARCHAR(75) NOT NULL,
`metaTitle` VARCHAR(100) NULL,
`slug` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
`summary` TINYTEXT NULL,
`type` SMALLINT(6) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`sku` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
`price` FLOAT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`discount` FLOAT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`quantity` SMALLINT(6) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`shop` TINYINT(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`createdAt` DATETIME NOT NULL,
`updatedAt` DATETIME NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`publishedAt` DATETIME NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`startsAt` DATETIME NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`endsAt` DATETIME NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`content` TEXT NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE INDEX `uq_slug` (`slug` ASC),
INDEX `idx_product_user` (`userId` ASC),
CONSTRAINT `fk_product_user`
FOREIGN KEY (`userId`)
REFERENCES `shop`.`user` (`id`)
ON DELETE NO ACTION
ON UPDATE NO ACTION);Product Meta
The Product Meta Table can be used to store additional information about products including the product banner URL etc. Below mentioned is the description of all the columns of the Product Meta Table.
| Id | The unique id to identify the product meta. |
| Product Id | The product id to identify the parent product. |
| Key | The key identifying the meta. |
| Content | The column used to store the product metadata. |
The Product Meta Table with the appropriate constraints is as shown below.
CREATE TABLE `shop`.`product_meta` (
`id` BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`productId` BIGINT NOT NULL,
`key` VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
`content` TEXT NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
INDEX `idx_meta_product` (`productId` ASC),
UNIQUE INDEX `uq_product_meta` (`productId` ASC, `key` ASC),
CONSTRAINT `fk_meta_product`
FOREIGN KEY (`productId`)
REFERENCES `shop`.`product` (`id`)
ON DELETE NO ACTION
ON UPDATE NO ACTION)
ENGINE = InnoDB;Product Review Table
In this section, we will design the Product Review Table to store the product reviews. Below mentioned is the description of all the columns of the Product Review Table.
| Id | The unique id to identify the product review. |
| Product Id | The product id to identify the parent product. |
| Parent Id | The parent id to identify the parent review. |
| Title | The review title. |
| Rating | The review rating. |
| Published | It can be used to identify whether the review is publicly available. |
| Created At | It stores the date and time at which the review is submitted. |
| Published At | It stores the date and time at which the review is published. |
| Content | The column used to store the review details. |
The Product Review Table with the appropriate constraints is as shown below.
CREATE TABLE `shop`.`product_review` (
`id` BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`productId` BIGINT NOT NULL,
`parentId` BIGINT NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`title` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
`rating` SMALLINT(6) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`published` TINYINT(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`createdAt` DATETIME NOT NULL,
`publishedAt` DATETIME NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`content` TEXT NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
INDEX `idx_review_product` (`productId` ASC),
CONSTRAINT `fk_review_product`
FOREIGN KEY (`productId`)
REFERENCES `shop`.`product` (`id`)
ON DELETE NO ACTION
ON UPDATE NO ACTION);
ALTER TABLE `shop`.`product_review`
ADD INDEX `idx_review_parent` (`parentId` ASC);
ALTER TABLE `shop`.`product_review`
ADD CONSTRAINT `fk_review_parent`
FOREIGN KEY (`parentId`)
REFERENCES `shop`.`product_review` (`id`)
ON DELETE NO ACTION
ON UPDATE NO ACTION;Category Table and Product Category Table
In this section, we will design the Category Table and Product Category Table to store the product categories and their mappings. Below mentioned is the description of all the columns of the Category Table.
| Id | The unique id to identify the category. |
| Parent Id | The parent id to identify the parent category. |
| Title | The category title. |
| Meta Title | The meta title to be used for browser title and SEO. |
| Slug | The category slug to form the URL. |
| Content | The column used to store the category details. |
The Category Table with the appropriate constraints is as shown below.
CREATE TABLE `shop`.`category` ( `id` BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `parentId` BIGINT NULL DEFAULT NULL, `title` VARCHAR(75) NOT NULL, `metaTitle` VARCHAR(100) NULL DEFAULT NULL, `slug` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL, `content` TEXT NULL DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`));
ALTER TABLE `shop`.`category`
ADD INDEX `idx_category_parent` (`parentId` ASC);
ALTER TABLE `shop`.`category`
ADD CONSTRAINT `fk_category_parent`
FOREIGN KEY (`parentId`)
REFERENCES `shop`.`category` (`id`)
ON DELETE NO ACTION
ON UPDATE NO ACTION;
Below mentioned is the description of all the columns of the Product Category Table.
| Product Id | The product id to identify the product. |
| Category Id | The category id to identify the category. |
The Product Category Table with the appropriate constraints is as shown below.
CREATE TABLE `shop`.`product_category` (
`productId` BIGINT NOT NULL,
`categoryId` BIGINT NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`productId`, `categoryId`),
INDEX `idx_pc_category` (`categoryId` ASC),
INDEX `idx_pc_product` (`productId` ASC),
CONSTRAINT `fk_pc_product`
FOREIGN KEY (`productId`)
REFERENCES `shop`.`product` (`id`)
ON DELETE NO ACTION
ON UPDATE NO ACTION,
CONSTRAINT `fk_pc_category`
FOREIGN KEY (`categoryId`)
REFERENCES `shop`.`category` (`id`)
ON DELETE NO ACTION
ON UPDATE NO ACTION);Tag Table and Product Tag Table
Similar to the category and product category tables, we can design the Tag Table and Product Tag Table. The major differences between the Category and Tag are listed below.
- The parentId column is not required in the Tag Table.
- The count of categories remains low since these can be used to form the Main Menu for navigational purposes. The tags can be more as compared to categories.
- Both categories and tags can be used to relate the products.
- One should assign only a few categories to a product whereas tags count can be more.
Cart Table and Cart Item Table
This section provides the tables to manage the virtual carts to store the user selection before creating the actual order. If the user cancels the payment or the payment fails, the same carts can be used as an abandoned cart by the marketing team to enquire about the buyers. A logged-in user can also be associated with the cart. Below mentioned is the description of all the columns of the Cart Table.
Notes: The Cart Table and Cart Item Table can be made optional if the Local Data, Session, or in-memory database like Redis is used to store the cart data. The same can be referred to create the order on payment success.
| Id | The unique id to identify the cart. |
| User Id | The user id to identify the user or buyer associated with the cart. |
| Session Id | The unique session id associated with the cart. |
| Token | The unique token associated with the cart to identify the cart over multiple sessions. The same token can also be passed to the Payment Gateway if required. |
| Status | The status of the cart can be New, Cart, Checkout, Paid, Complete, and Abandoned. |
| First Name | The first name of the user. |
| Middle Name | The middle name of the user. |
| Last Name | The last name of the user. |
| Mobile | The mobile number of the user. |
| The email of the user. | |
| Line 1 | The first line to store address. |
| Line 2 | The second line to store address. |
| City | The city of the address. |
| Province | The province of the address. |
| Country | The country of the address. |
| Created At | It stores the date and time at which the cart is created. |
| Updated At | It stores the date and time at which the cart is updated. |
| Content | The column used to store the additional details of the cart. |
The Cart Table with the appropriate constraints is as shown below.
CREATE TABLE `shop`.`cart` (
`id` BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`userId` BIGINT NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`sessionId` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
`token` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
`status` SMALLINT(6) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`firstName` VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`middleName` VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`lastName` VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`mobile` VARCHAR(15) NULL,
`email` VARCHAR(50) NULL,
`line1` VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`line2` VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`city` VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`province` VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`country` VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`createdAt` DATETIME NOT NULL,
`updatedAt` DATETIME NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`content` TEXT NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
INDEX `idx_cart_user` (`userId` ASC),
CONSTRAINT `fk_cart_user`
FOREIGN KEY (`userId`)
REFERENCES `shop`.`user` (`id`)
ON DELETE NO ACTION
ON UPDATE NO ACTION);Below mentioned is the description of all the columns of the Cart Item Table.
| Id | The unique id to identify the cart item. |
| Product Id | The product id to identify the product associated with the cart item. |
| Cart Id | The cart id to identify the cart associated with the cart item. |
| SKU | The SKU of the product while purchasing it. |
| Price | The price of the product while purchasing it. |
| Discount | The discount of the product while purchasing it. |
| Quantity | The quantity of the product selected by the user. |
| Active | The flag to identify whether the product is active on the cart. It can be used to avoid the same product being added to the same cart multiple times. |
| Created At | It stores the date and time at which the cart item is created. |
| Updated At | It stores the date and time at which the cart item is updated. |
| Content | The column used to store the additional details of the cart item. |
The Cart Item Table with the appropriate constraints is as shown below.
CREATE TABLE `shop`.`cart_item` (
`id` BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`productId` BIGINT NOT NULL,
`cartId` BIGINT NOT NULL,
`sku` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
`price` FLOAT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`discount` FLOAT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`quantity` SMALLINT(6) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`active` TINYINT(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`createdAt` DATETIME NOT NULL,
`updatedAt` DATETIME NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`content` TEXT NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
INDEX `idx_cart_item_product` (`productId` ASC),
CONSTRAINT `fk_cart_item_product`
FOREIGN KEY (`productId`)
REFERENCES `shop`.`product` (`id`)
ON DELETE NO ACTION
ON UPDATE NO ACTION);
ALTER TABLE `shop`.`cart_item`
ADD INDEX `idx_cart_item_cart` (`cartId` ASC);
ALTER TABLE `shop`.`cart_item`
ADD CONSTRAINT `fk_cart_item_cart`
FOREIGN KEY (`cartId`)
REFERENCES `shop`.`cart` (`id`)
ON DELETE NO ACTION
ON UPDATE NO ACTION;
Order Table and Order Item Table
This section provides the tables to manage the store orders. A logged-in user can also be associated with the order. Below mentioned is the description of all the columns of the Order Table.
| Id | The unique id to identify the order. |
| User Id | The user id to identify the user or buyer associated with the order. |
| Session Id | The unique session id associated with the order. |
| Token | The unique token associated with the order to identify it over multiple sessions. The same token can also be passed to the Payment Gateway if required. |
| Status | The status of the order can be New, Checkout, Paid, Failed, Shipped, Delivered, Returned, and Complete. |
| Sub Total | The total price of the Order Items. |
| Item Discount | The total discount of the Order Items. |
| Tax | The tax on the Order Items. |
| Shipping | The shipping charges of the Order Items. |
| Total | The total price of the Order including tax and shipping. It excludes the items discount. |
| Promo | The promo code of the Order. |
| Discount | The total discount of the Order based on the promo code or store discount. |
| Grand Total | The grand total of the order to be paid by the buyer. |
| First Name | The first name of the user. |
| Middle Name | The middle name of the user. |
| Last Name | The last name of the user. |
| Mobile | The mobile number of the user. |
| The email of the user. | |
| Line 1 | The first line to store address. |
| Line 2 | The second line to store address. |
| City | The city of the address. |
| Province | The province of the address. |
| Country | The country of the address. |
| Created At | It stores the date and time at which the order is created. |
| Updated At | It stores the date and time at which the order is updated. |
| Content | The column used to store the additional details of the order. |
The Order Table with the appropriate constraints is as shown below.
CREATE TABLE `shop`.`order` (
`id` BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`userId` BIGINT NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`sessionId` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
`token` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
`status` SMALLINT(6) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`subTotal` FLOAT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`itemDiscount` FLOAT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`tax` FLOAT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`shipping` FLOAT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`total` FLOAT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`promo` VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`discount` FLOAT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`grandTotal` FLOAT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`firstName` VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`middleName` VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`lastName` VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`mobile` VARCHAR(15) NULL,
`email` VARCHAR(50) NULL,
`line1` VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`line2` VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`city` VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`province` VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`country` VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`createdAt` DATETIME NOT NULL,
`updatedAt` DATETIME NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`content` TEXT NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
INDEX `idx_order_user` (`userId` ASC),
CONSTRAINT `fk_order_user`
FOREIGN KEY (`userId`)
REFERENCES `shop`.`user` (`id`)
ON DELETE NO ACTION
ON UPDATE NO ACTION);
Below mentioned is the description of all the columns of the Order Item Table.
| Id | The unique id to identify the ordered item. |
| Product Id | The product id to identify the product associated with the ordered item. |
| Order Id | The order id to identify the order associated with the ordered item. |
| SKU | The SKU of the product while purchasing it. |
| Price | The price of the product while purchasing it. |
| Discount | The discount of the product while purchasing it. |
| Quantity | The quantity of the product selected by the user. |
| Created At | It stores the date and time at which the ordered item is created. |
| Updated At | It stores the date and time at which the ordered item is updated. |
| Content | The column used to store the additional details of the ordered item. |
The Order Item Table with the appropriate constraints is as shown below.
CREATE TABLE `shop`.`order_item` (
`id` BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`productId` BIGINT NOT NULL,
`orderId` BIGINT NOT NULL,
`sku` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
`price` FLOAT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`discount` FLOAT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`quantity` SMALLINT(6) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`createdAt` DATETIME NOT NULL,
`updatedAt` DATETIME NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`content` TEXT NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
INDEX `idx_order_item_product` (`productId` ASC),
CONSTRAINT `fk_order_item_product`
FOREIGN KEY (`productId`)
REFERENCES `shop`.`product` (`id`)
ON DELETE NO ACTION
ON UPDATE NO ACTION);
ALTER TABLE `shop`.`order_item`
ADD INDEX `idx_order_item_order` (`orderId` ASC);
ALTER TABLE `shop`.`order_item`
ADD CONSTRAINT `fk_order_item_order`
FOREIGN KEY (`orderId`)
REFERENCES `shop`.`order` (`id`)
ON DELETE NO ACTION
ON UPDATE NO ACTION;
Transaction Table
We also need a transaction table to track the order payments made by the buyer and for bookkeeping. We can also use the same table to record the partial or full refund of the order. Below mentioned is the description of all the columns of the Transaction Table.
| Id | The unique id to identify the transaction. |
| User Id | The user id to identify the user associated with the transaction. |
| Order Id | The order id to identify the order associated with the transaction. |
| Code | The payment id provided by the payment gateway. |
| Type | The type of order transaction can be either Credit or Debit. |
| Mode | The mode of the order transaction can be Offline, Cash On Delivery, Cheque, Draft, Wired, and Online. |
| Status | The status of the order transaction can be New, Cancelled, Failed, Pending, Declined, Rejected, and Success. |
| Created At | It stores the date and time at which the order transaction is created. |
| Updated At | It stores the date and time at which the order transaction is updated. |
| Content | The column used to store the additional details of the transaction. |
The Transaction Table with the appropriate constraints is as shown below.
CREATE TABLE `shop`.`transaction` (
`id` BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`userId` BIGINT NOT NULL,
`orderId` BIGINT NOT NULL,
`code` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
`type` SMALLINT(6) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`mode` SMALLINT(6) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`status` SMALLINT(6) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
`createdAt` DATETIME NOT NULL,
`updatedAt` DATETIME NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`content` TEXT NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
INDEX `idx_transaction_user` (`userId` ASC),
CONSTRAINT `fk_transaction_user`
FOREIGN KEY (`userId`)
REFERENCES `shop`.`user` (`id`)
ON DELETE NO ACTION
ON UPDATE NO ACTION);
ALTER TABLE `shop`.`transaction`
ADD INDEX `idx_transaction_order` (`orderId` ASC);
ALTER TABLE `shop`.`transaction`
ADD CONSTRAINT `fk_transaction_order`
FOREIGN KEY (`orderId`)
REFERENCES `shop`.`order` (`id`)
ON DELETE NO ACTION
ON UPDATE NO ACTION;
Address Table
An address table can be used to avoid the redundant columns in the Cart and Order table depending on the actual implementation. It can be directly mapped to the Cart Table and Order Table using the appropriate foreign keys.
Summary
In this tutorial, we have discussed the database design of an Online Shopping Cart to store the users and manage product inventory. It also provided the database design to manage the cart, store the cart items, and manage the orders on an online shop. The Simplified Online Shopping Flowchart can be referred to implement a Shopping Cart.
You may submit your comments to join the discussion. You may also be interested in designing the database of the Blog and Poll & Survey applications. The complete database schema is also available on GitHub.

