We can containerize our applications using Docker to have a separate installation of the required packages with the application-specific versions independent of the underlying operating system. We can use Docker Containers to make our application portable so that we can simply move it to another system having docker. This tutorial provides all the steps to containerize a PHP application using Apache Web Server as the webserver and either MySQL or MongoDB as the database server.
Prerequisites
Windows - How To Install WSL 2 (Windows Subsystem for Linux) with Ubuntu On Windows 10 and How To Install Docker Desktop On Windows 10. Optionally you may follow How To Change Docker Data Path On Windows 10.
Ubuntu - How To Install Docker Engine on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
macOS - How To Install Docker Desktop On Mac
Install PHP and Apache Web Server
Create a directory to store your project-specific files. I have created the directory helloworld to store all the project files. Now create the file docker-compose.yml at the root of your project directory as shown below.
# docker-compose.yml
version: "3.8"
services:
apache:
container_name: apache
build: ./docker/apache
links:
- php
ports:
- "80:80"
volumes:
- ./src:/usr/local/apache2/htdocs
php:
container_name: php
build: ./docker/php
ports:
- "9000:9000"
volumes:
- ./src:/usr/local/apache2/htdocs
working_dir: /usr/local/apache2/htdocsNow create the directories - docker and src within the project root directory. Also, create two directories within the docker directory i.e. php and apache.
Create the Dockerfile within the PHP directory as shown below.
# docker/php/Dockerfile FROM php:8.1-fpm
Create the Dockerfile within the Apache directory as shown below.
# docker/apache/Dockerfile FROM httpd:2.4.51
Create the index.php file within the src directory as shown below.
# src/index.php <?php echo phpinfo();
We also need to configure the Virtual Host to pass the PHP requests to PHP-FPM vial port 9000. Now, create the default configuration file as shown below.
# docker/apache/helloworld.apache.conf LoadModule deflate_module /usr/local/apache2/modules/mod_deflate.so LoadModule proxy_module /usr/local/apache2/modules/mod_proxy.so LoadModule proxy_fcgi_module /usr/local/apache2/modules/mod_proxy_fcgi.so
<VirtualHost *:80> ProxyPassMatch ^/(.*\.php(/.*)?)$ fcgi://php:9000/usr/local/apache2/htdocs/$1 DocumentRoot /usr/local/apache2/htdocs <Directory /usr/local/apache2/htdocs> Options -Indexes +FollowSymLinks DirectoryIndex index.php AllowOverride All Require all granted </Directory> </VirtualHost>
Now, update the Dockerfile within the Apache directory as shown below.
# docker/apache/Dockerfile FROM httpd:2.4.51
COPY helloworld.apache.conf /usr/local/apache2/conf/helloworld.apache.conf
RUN echo "Include /usr/local/apache2/conf/helloworld.apache.conf" \ >> /usr/local/apache2/conf/httpd.conf
After creating all the directories and files, the directory structure should be similar as shown below.
helloworld
-- docker
-- php
-- Dockerfile
-- apache
-- Dockerfile
-- helloworld.apache.conf
-- src
-- index.php
-- docker-compose.yml Now, run the command docker-compose build to build the images for PHP and Apache Web Server.
# Build cd <path to project>/helloworld docker-compose build
# Output Building php [+] Building 3.9s (6/6) FINISHED => [internal] load build definition from Dockerfile 0.1s => => transferring dockerfile: 55B 0.0s => [internal] load .dockerignore 0.1s => => transferring context: 2B 0.0s => [internal] load metadata for docker.io/library/php:8.1-fpm 3.6s => [auth] library/php:pull token for registry-1.docker.io 0.0s => CACHED [1/1] FROM docker.io/library/php:8.1-fpm@sha256:c884ad419ce99d3136cd02a56f7ca84009fa5a50637e96d20acdd7 0.0s => exporting to image 0.1s => => exporting layers 0.0s => => writing image sha256:dd8e9ace979d52b810014bd90565f9bf60ffdbb754af263b1eb3b2bb5cc88648 0.0s => => naming to docker.io/library/helloworld_php 0.0s
Use 'docker scan' to run Snyk tests against images to find vulnerabilities and learn how to fix them Building apache [+] Building 4.3s (9/9) FINISHED => [internal] load build definition from Dockerfile 0.1s => => transferring dockerfile: 250B 0.0s => [internal] load .dockerignore 0.1s => => transferring context: 2B 0.0s => [internal] load metadata for docker.io/library/httpd:2.4.51 3.9s => [auth] library/httpd:pull token for registry-1.docker.io 0.0s => [internal] load build context 0.1s => => transferring context: 586B 0.0s => [1/3] FROM docker.io/library/httpd:2.4.51@sha256:fba8a9f4290180ceee5c74638bb85ff21fd15961e6fdfa4def48e1882051 0.0s => CACHED [2/3] COPY helloworld.apache.conf /usr/local/apache2/conf/helloworld.apache.conf 0.0s => CACHED [3/3] RUN echo "Include /usr/local/apache2/conf/helloworld.apache.conf" >> /usr/local/apache2/conf 0.0s => exporting to image 0.1s => => exporting layers 0.0s => => writing image sha256:163fe8f15637311df7bb05aab39101a1505723c105461d253539939da9a14c36 0.0s => => naming to docker.io/library/helloworld_apache 0.0s
Use 'docker scan' to run Snyk tests against images to find vulnerabilities and learn how to fix them
After completing the build, we can run the application using the command shown below.
# Launch Application docker-compose up
# Output Creating network "helloworld_default" with the default driver Creating php ... done Creating apache ... done Attaching to php, apache
Now open the browser and enter the URL - http://localhost/index.php. It should show the output of index.php as shown in Fig.1.
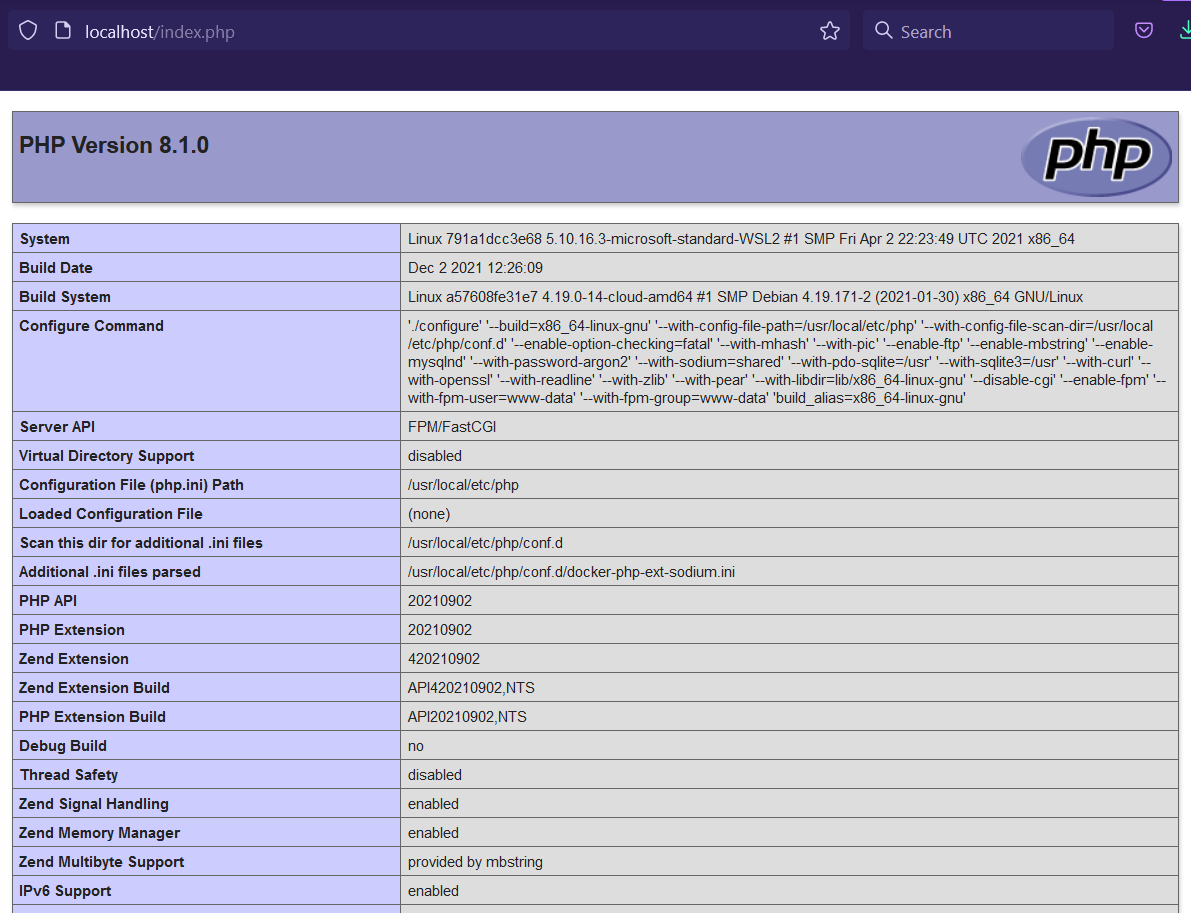
Fig 1
Press Ctrl + C to stop the containers.
Install MySQL and phpMyAdmin
In this step, we will continue with our previous step and install MySQL and phpMyAdmin. We will also access the MySQL database from the PHP code using PDO. Now, update the docker-compose.yml as shown below.
# docker-compose.yml
version: "3.8"
services:
apache:
container_name: apache
build: ./docker/apache
links:
- php
ports:
- "80:80"
volumes:
- ./src:/usr/local/apache2/htdocs
php:
container_name: php
build: ./docker/php
links:
- mysql
ports:
- "9000:9000"
volumes:
- ./src:/usr/local/apache2/htdocs
working_dir: /usr/local/apache2/htdocs
mysql:
image: mysql:8.0.27
container_name: mysql
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: '<root-password>'
MYSQL_DATABASE: helloworld
MYSQL_USER: helloworld
MYSQL_PASSWORD: '<db-password>'
ports:
- "3306:3306"
volumes:
- ./database/mysql:/var/lib/mysql
phpmyadmin:
image: phpmyadmin/phpmyadmin
container_name: pma
links:
- mysql
environment:
PMA_HOST: mysql
PMA_PORT: 3306
PMA_ARBITRARY: 1
restart: always
ports:
- 8085:80Now, run the command docker-compose build to build the application.
# Build cd <path to project>/helloworld docker-compose build
# Output mysql uses an image, skipping phpmyadmin uses an image, skipping Building php .... .... => => naming to docker.io/library/helloworld_apache 0.0s
Use 'docker scan' to run Snyk tests against images to find vulnerabilities and learn how to fix them
We also need to run the command docker-compose up to launch the application as shown below. It will pull the MySQL and phpMyAdmin images and take time for the first time. The subsequent launches will be faster.
# Launch Application docker-compose up
# Output Pulling mysql (mysql:8.0.27)... 8.0.27: Pulling from library/mysql ffbb094f4f9e: Pull complete df186527fc46: Pull complete fa362a6aa7bd: Pull complete 5af7cb1a200e: Pull complete .... .... Status: Downloaded newer image for mysql:8.0.27 Pulling phpmyadmin (phpmyadmin/phpmyadmin:)... latest: Pulling from phpmyadmin/phpmyadmin 69692152171a: Pull complete 2040822db325: Pull complete .... .... 2e982de2b8e5: Pull complete Digest: sha256:382dedf6b43bf3b6c6c90f355b4dda660beb3e099dqw1bb3241170e54fca6d59 Status: Downloaded newer image for phpmyadmin/phpmyadmin:latest .... .... Creating mysql ... done Recreating php ... done Creating pma ... done Recreating apache ... done Attaching to mysql, pma, php, apache .... ....
Now, try to access phpMyAdmin from the Browser using the URL http://localhost:8085. It should show the phpMyAdmin home page as shown in Fig.2.

Fig 2
Now, login to phpMyAdmin using the username as root and the root password configured in the docker-compose.yml. Also, leave the server blank. It should show the phpMyAdmin home page as shown in Fig 3.
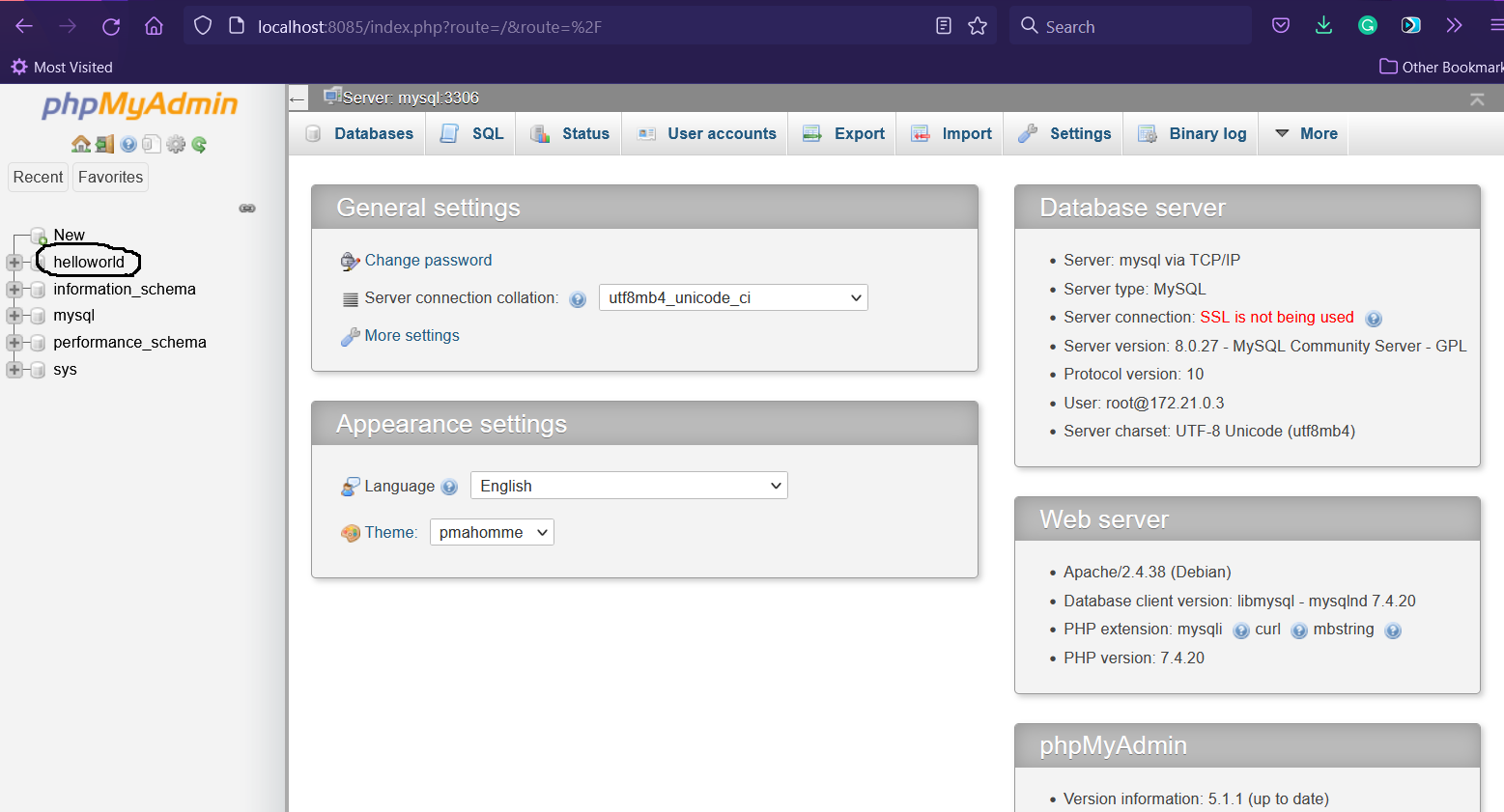
Fig 3
Press Ctrl + C to stop the containers.
# Press Ctrl + C Gracefully stopping... (press Ctrl+C again to force) Stopping apache ... done Stopping php ... done Stopping pma ... done Stopping mysql ... done
Now, install the PHP extensions to access MySQL from the PHP source files by updating the Dockerfile as shown below.
# docker/php/Dockerfile FROM php:8.1
RUN apt-get update RUN docker-php-ext-install pdo pdo_mysql mysqli
Also, run the build and up commands to again build the application and launch it. We can test MySQL connectivity using PHP as shown below. You can also follow How To Connect MySQL Database With PHP.
# src/mysql.php <?php $hostname = "mysql"; $dbname = "helloworld"; $username = "helloworld"; $password = "db-password";
try { $conn = new PDO( "mysql:host=$hostname;dbname=$dbname", $username, $password );
// Configure PDO error mode $conn->setAttribute( PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION );
echo "Connected successfully"; } catch( PDOException $e ) {
echo "Failed to connect: " . $e->getMessage(); }
// Perform database operations
// Close the connection $conn = null;
If we open the PHP file using the URL http://localhost/mysql.php, it should show the output as shown in Fig 4.

Fig 4
This completes the installation and configuration of MySQL and phpMyAdmin.
Press Ctrl + C to stop the containers.
Install MongoDB and MongoDB Express
In this step, we will continue with our previous step and install MongoDB and MongoDB Express. Now, update the docker-compose.yml as shown below.
# docker-compose.yml
version: "3.8"
services:
apache:
container_name: apache
build: ./docker/apache
links:
- php
ports:
- "80:80"
volumes:
- ./src:/usr/local/apache2/htdocs
php:
container_name: php
build: ./docker/php
links:
- mysql
- mongo
ports:
- "9000:9000"
volumes:
- ./src:/usr/local/apache2/htdocs
working_dir: /usr/local/apache2/htdocs
mysql:
image: mysql:8.0.27
container_name: mysql
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: 'root-password'
MYSQL_DATABASE: helloworld
MYSQL_USER: helloworld
MYSQL_PASSWORD: 'database-password'
ports:
- "3306:3306"
volumes:
- ./database/mysql:/var/lib/mysql
phpmyadmin:
image: phpmyadmin/phpmyadmin
container_name: pma
links:
- mysql
environment:
PMA_HOST: mysql
PMA_PORT: 3306
PMA_ARBITRARY: 1
restart: always
ports:
- 8085:80
mongo:
image: mongo:5.0
container_name: mongo
environment:
- MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME=root
- MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD=password
restart: unless-stopped
ports:
- "27017:27017"
volumes:
- ./database/mongodb/db:/data/db
- ./database/mongodb/dev.archive:/Databases/dev.archive
- ./database/mongodb/production:/Databases/production
mongo-express:
image: mongo-express
container_name: mexpress
environment:
- ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_ADMINUSERNAME=root
- ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_ADMINPASSWORD=password
- ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_URL=mongodb://root:password@mongo:27017/?authSource=admin
- ME_CONFIG_BASICAUTH_USERNAME=mexpress
- ME_CONFIG_BASICAUTH_PASSWORD=mexpress
links:
- mongo
restart: unless-stopped
ports:
- "8081:8081"Replace the root password while configuring the docker-compose.yml. Also, install the PHP extensions to access MongoDB from the PHP source files by updating the Dockerfile as shown below.
# docker/php/Dockerfile FROM php:8.1
RUN apt-get update RUN docker-php-ext-install pdo pdo_mysql mysqli
RUN apt-get install -y autoconf pkg-config libssl-dev RUN pecl install mongodb RUN echo "extension=mongodb.so" >> /usr/local/etc/php/conf.d/mongodb.ini
Now, run the build and up commands to again build the application and launch it. We can access MongoDB using the URL - http://localhost:8081. It will ask for the basic authentication configured by us. The home page should be similar as shown below.

Fig 5
This completes the installation and configuration of MongoDB for PHP.
Summary
This tutorial provided all the steps to containerize PHP with Apache Web Server, MySQL, phpMyAdmin, MongoDB, and MongoDB Express using Docker containers.

